Dbs101_flippedclass3
Null values and Set operations in SQL.
Summary on what I did in flipped class
The Flipped Class session focused on null values and set operations in SQL. Group formation was conducted with a size of 6-7 students, resulting in the creation of 4 groups labeled as G1 to G4. Expert Groups were formed, with two groups each, aimed at enabling deeper learning of specific tools and facilitating subsequent sharing with home groups. Expert Group (G1, G2) worked on Set operations in SQL, while Expert Group (G3, G4) focused on Null values in SQL. I was in G4, where we studied null values in SQL. Later, we explained null values in SQL to our respective home groups, while they, in turn, explained set operations in SQL.
Things Learned in Flipped class
Null Values
In flipped class we learned about the null values and set operators. Firstly a null value is distinct from an empty field filled with spaces. It occurs when a field is left blank during record creation. Setting a NULL value is appropriate when the actual value is unknown or meaningless. NULL is not equivalent to zero for numeric data types or to spaces for character data types. If a column contains a NULL value, SQL constraints such as UNIQUE, FOREIGN KEY, and CHECK will be ignored. To check for null values, we use “IS NULL” and “IS NOT NULL.” “IS NULL” returns true if the value is NULL, while “IS NOT NULL” returns true if the value is not NULL.
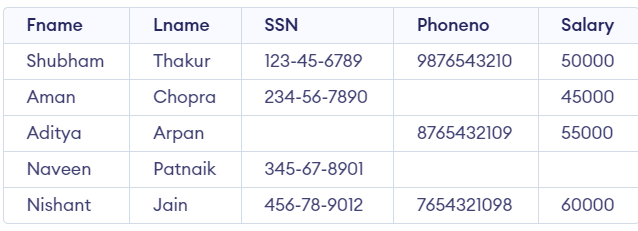
Example
IS NULL Operator
Suppose we find the Fname and Lname of the Employee having no Super_ssn then the query will be
SELECT Fname, Lname FROM Employee WHERE SSN IS NULL;
Output:
IS NOT NULL Operator
Now if we find the Count of number of Employees having SSNs.
Query:
SELECT COUNT(*) AS Count FROM Employee WHERE SSN IS NOT NULL;
Output:
Set operators
Set operators are special type of operators which are used to combine the result of two queries. Types of set operators are union, union all, intersect and minus. SQL Union combines the results of multiple SELECT queries. It requires that the number of columns and their data types match across tables. Union eliminates duplicate rows from the result set. SQL Union All operation is equal to the Union operation. It returns the set without removing duplication and sorting the data Intersect combines two SELECT statements, returning only common rows. Data types and column numbers must match. It removes duplicates and arranges data in ascending order by default. Minus combines results of two SELECT statements. The Minus operator shows rows in the first query absent in the second. It removes duplicates and arranges data in ascending order by default.
Feedback on Flipped Class
Everything went well this time, and I now have a solid understanding of null values and set operators. However, a drawback of this session was that we didn’t practically check for null values or utilize the set operators. I would be grateful if, in upcoming sessions, we could incorporate practical exercises, as SQL is primarily about applying concepts on the computer rather than just reading articles and notes.